Guía nº 2 de problemas resueltos de funciones cuadráticas
Resolver los siguientes ejercicios
� Ver resolución de los ejercicios al pie de la página
Problema nº 1
Hallar las raíces de las siguientes ecuaciones:
a) x² - 16 = 0
b) 2·x² + 30·x = 0
c) x² - 7·x - 18 = 0
d) 2·x² - 16·x + 30 = 0
e) 20·x² = 0
f) 6·x - 9 = -x²
g) x² + 8·x + 12 = 0
h) x² - 1 = 0
• Respuesta:
a) x₁ = 4; x₂ = -4;
b) x₁ = 0; x₂ = -15;
c) x₁ = 9; x₂ = -2;
d) x₁ = 5; x₂ = 3;
e) x₁ = x₂ = 0;
f) 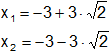 ;
;
g) x₁ = -2; x₂ = -6;
h) x₁ = 1; x₂ = -1
Problema nº 2
Hallar las raíces de las siguientes ecuaciones:
a) 4·x⁴ = 37·x² - 9
b) x² - 9·x = -18·x
c) x⁴ - 4·x² + 3 = 0
d) 16·x² - 50·x = 0
e) x² - 10·x - 25 = 0
f) 3·x² + 5·x = 8
g) 4·x⁴ + 16·x² = 0
• Respuesta:a) x₁ = 3; x₂ = -3; x₃ = ½; x₄ = -½;
b) x₁ = 0; x₂ = -9;
c) ![]() ; x₃ = 1; x₄ = -1;
; x₃ = 1; x₄ = -1;
d) x₁ = 0; x₂ = 25/8;
e) 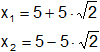
f) x₁ = 1; x₂ = -8/3;
g) x₁ = x₂ = 0; x₃ = ∉ ℜ; x₄ = ∉ ℜ
Problema nº 3
Hallar las intersecciones con los ejes, los vértices y graficar las siguientes funciones:
a) y = x² - 12·x + 32
b) y = x² - x - 12
c) x² - 4·x - 2·y + 4 = 0
d) y = -x² + x + 6
e) ![]()
f) ![]()
g) ![]()
h) x² + 8·y = 0
i) ![]()
j) y = x² - 6·y - 2
k) x² - 4·y = 0
l) y = 2·x² - 7·x + 5
• Respuesta:
a)
x₁ = 8
x₂ = 4
y = 32
V = (6; -4)
b)
x₁ = 4
x₂ = -3
y = -12
![]()
c)
x1,2 = 2
y = 2
V = (2; 0)
d)
x₁ = 3
x₂ = -2
y = 6
![]()
e)
x₁ = ½
x₂ = -1
y = -½
![]()
f)
x₁ = 2
x₂ = ½
y = 1
![]()
g)
x₁ = x₂ = 2
y = -1
V = (2; 0)
h)
x₁ = x₂ = 0
y = 0
V = (0; 0)
i)
![]()
![]()
V = (1; -¼)
j)
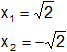
![]()
![]()
k)
x₁ = x₂ = 0
y = 0
V = (0; 0)
l)
x₁ = 5/2
x₂ = 1
y = 5
![]()
Autor: Ricardo Santiago Netto. Argentina
Problemas resueltos:
Parábolas, cómo hallar las raíces y el vértice.